The java.lang.Class have some useful methods for getting information about class at run time. In this example I am going to get the all field name and variable name present in particular class using reflection.
import
java.lang.reflect.Field;
import
java.lang.reflect.Method;
class TestReflection
{
public int field1;
public int field2;
public void addField() {
System.out.println("Addition
of two fields: " + (field1 + field2));
}
}
public class ReflectionDemo
{
public static void main(String[]
args) {
try{
TestReflection
testReflection = new TestReflection();
Method
methodNames[] = testReflection.getClass().getMethods();
Field
fieldName[] = testReflection.getClass().getFields();
for(int
i=0;i<methodNames.length;i++) {
System.out.println("Method
Name: " + methodNames[i].toString());
}
System.out.println("*************************");
for(int
i=0;i<fieldName.length;i++) {
System.out.println("Field
Name: " + fieldName[i].toString());
}
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
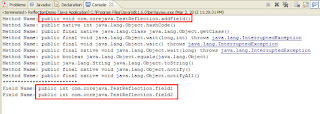
In this example I have created the two class for implementing reflection. The class TestReflection have two integer field field1,field2 and one method addField() for adding these two integer. In main class, I have created the one object for TestReflection class. After that I get the Class object of testReflection using getClass() method. Finally I get the all method names and field names using Class.getMethods() and Class.getFields().
Result:
Comments