I assume you have configured your eclipse or STS for android application development. If you not configured then follow up my previous tutorial.
1. For creating new android project open your eclipse or STS and go to File - New then choose Others. Select Android Project option and click Next.
2. Choose your android target version. It's based on your requirement, here I have choose my android version as 2.1. and click Next.
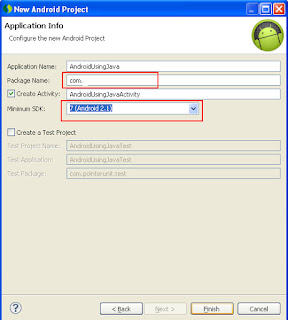
3. Specify your Java package name, Choose your minimum SDK version as 7 and click Finish.
1. For creating new android project open your eclipse or STS and go to File - New then choose Others. Select Android Project option and click Next.
2. Choose your android target version. It's based on your requirement, here I have choose my android version as 2.1. and click Next.
4. The final folder structure will be looks like this.
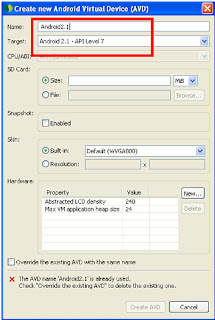
5. For running this application you have to configure your "Android Virtual Driver Manager". This is one time process for entire application development. For configuring this one, Choose Window -- AVD Manager or Click AVD icons present in your eclipse or STS.
6. Click New button, Choose your target as same you gave during project creation time and give some name. Give some 100 MB size as SD card size and click Create AVD buttons.
7. Ok now you have successfully created a new android emulator for testing our application. For running application, Right click on project root folder, Choose "Run As" option and click "Run Configuration".
8. Click Target option, and select your target then click "Run".
9. Now you will get result like this.
Now you get a confusion, I didn't write any code then how it displayed this message?
10. Open your main.xml file present in layout folder and see the XML code. By default whenever you create android application the TextView component is created, this have the value as "Hello World" with application name. Just modify the android:text property value as @string/Hello World.
11. Now run the application using emulator, you got the result like this.
Yes, You have successfully created your first android application. For testing with real phone you have to install the .apk file present in bin folder into your android phone.











Comments