In this tutorial I am going to explain about the basic input field such a as edit field, password field, multiline edit field, email field, etc.., creation in android.
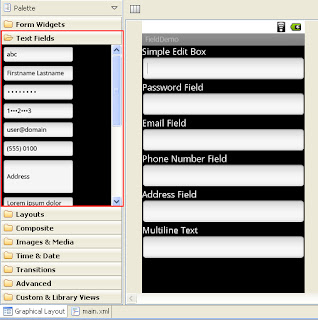
Create a one new Android project and open the main.xml file in Layout window. In palette window you can able to see varies type of input field. Just drag and drop some components in to your main screen. Here I have created some basic input fields, see the below screen shot.
For your reference, I have included the source code of my main.xml file.
<?xml
version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Simple Edit Box"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Password
Field"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPassword"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Email
Field"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textEmailAddress"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Phone Number
Field"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText4"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="phone"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Address
Field"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText5"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPostalAddress"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Multiline
Text"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText6"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textMultiLine"
/>
</LinearLayout>
Now run the application using emulator, you can able to get the result like this.

Comments